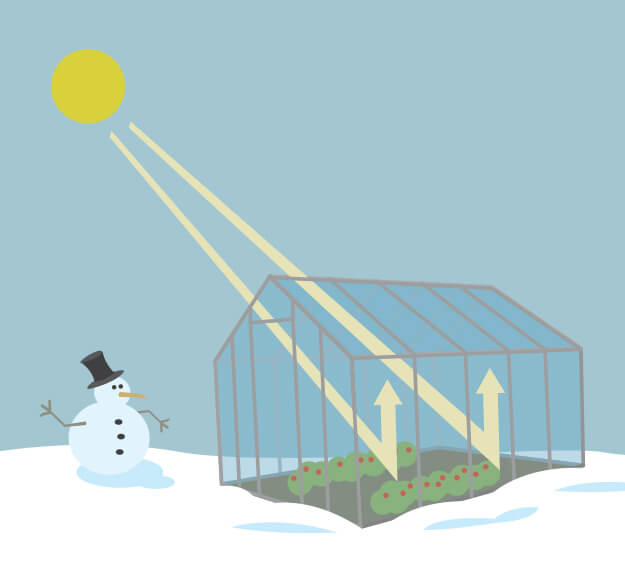
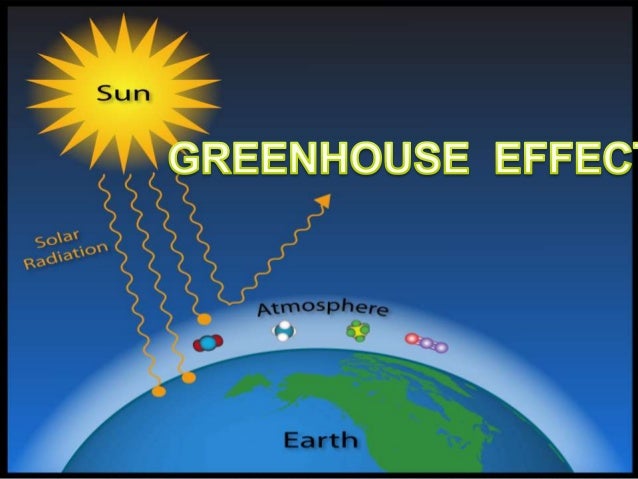
The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect worksThe greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would beA greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm

Climate And Greenhouse Effect Umweltbundesamt
Greenhouse effect coffee
Greenhouse effect coffee-In short it is the natural process that warms the Earth's surface The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouseThe Greenhouse Effect is a theory of Supreme Court justices' behavior, first proposed by Hoover Institution economist Thomas Sowell and popularized by DC Court of Appeals Senior Judge Laurence Silberman in a speech to The Federalist Society in 1992 Greenhouse refers to Linda Greenhouse, a Pulitzer Prize winning reporter who covered the Supreme Court for the New York




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
A greenhouse is for growing plants It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight But why not just put the plants outside?A stronger greenhouse effect will warm the ocean and partially melt glaciers and ice sheets, increasing sea level Ocean water also will expand if it warms, contributing further to sea level rise Outside of a greenhouse, higher atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) levels can have both positive and negative effects on crop yieldsThe 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effect A term used to describe the heating of the atmosphere owing to the presence of carbon dioxide and other gas es Without the presence of these gases, heat from the sun would return to space in the form of infrared radiationGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthDefine greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth Some heat is reflected back through the atmosphere, while some is
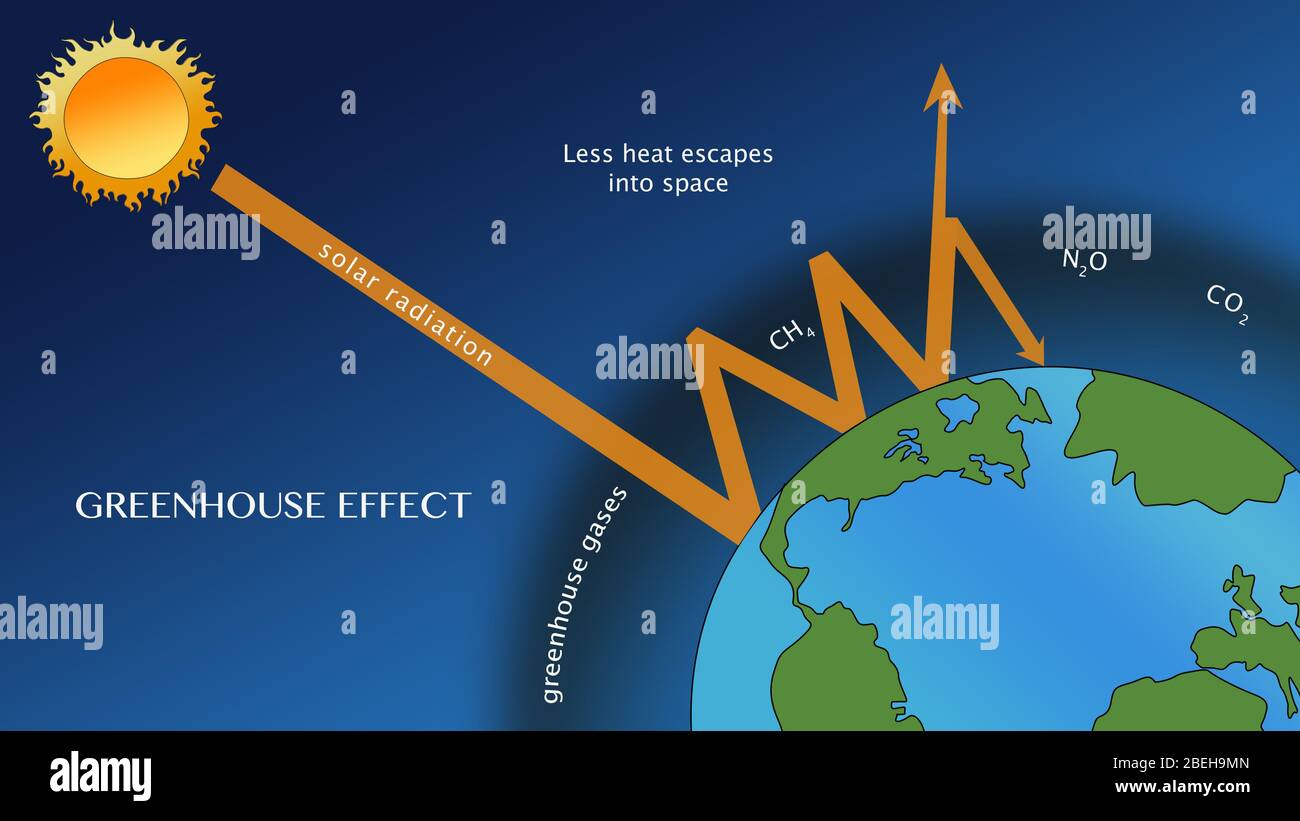
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)The term "greenhouse effect" is mentioned a lot when we talk about climate change But what exactly does it mean?The greenhouse effect is what keeps our planet warm enough to support life




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Amnh




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Climate Change And Their Relationships Sgk Planet
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiateThe greenhouse effect is the process in which the emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere warms a planet's surface The name comes from an analogy with the warming ofWater vapor is known to be Earth's most abundant greenhouse gas, but the extent of its contribution to global warming has been debated Using recent NASA satellite data, researchers have estimated more precisely than ever the heattrapping effect of water in the air, validating the role of the gas as a critical component of climate change
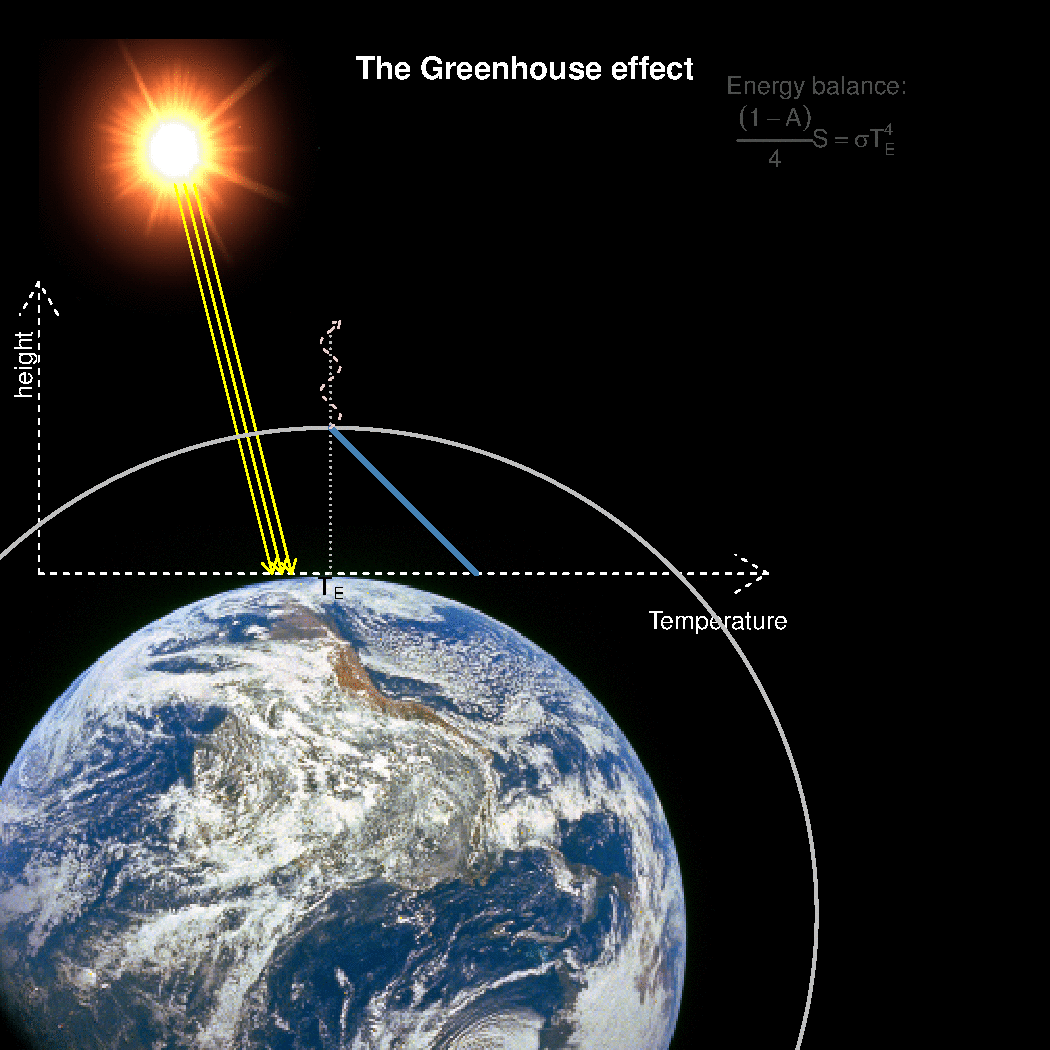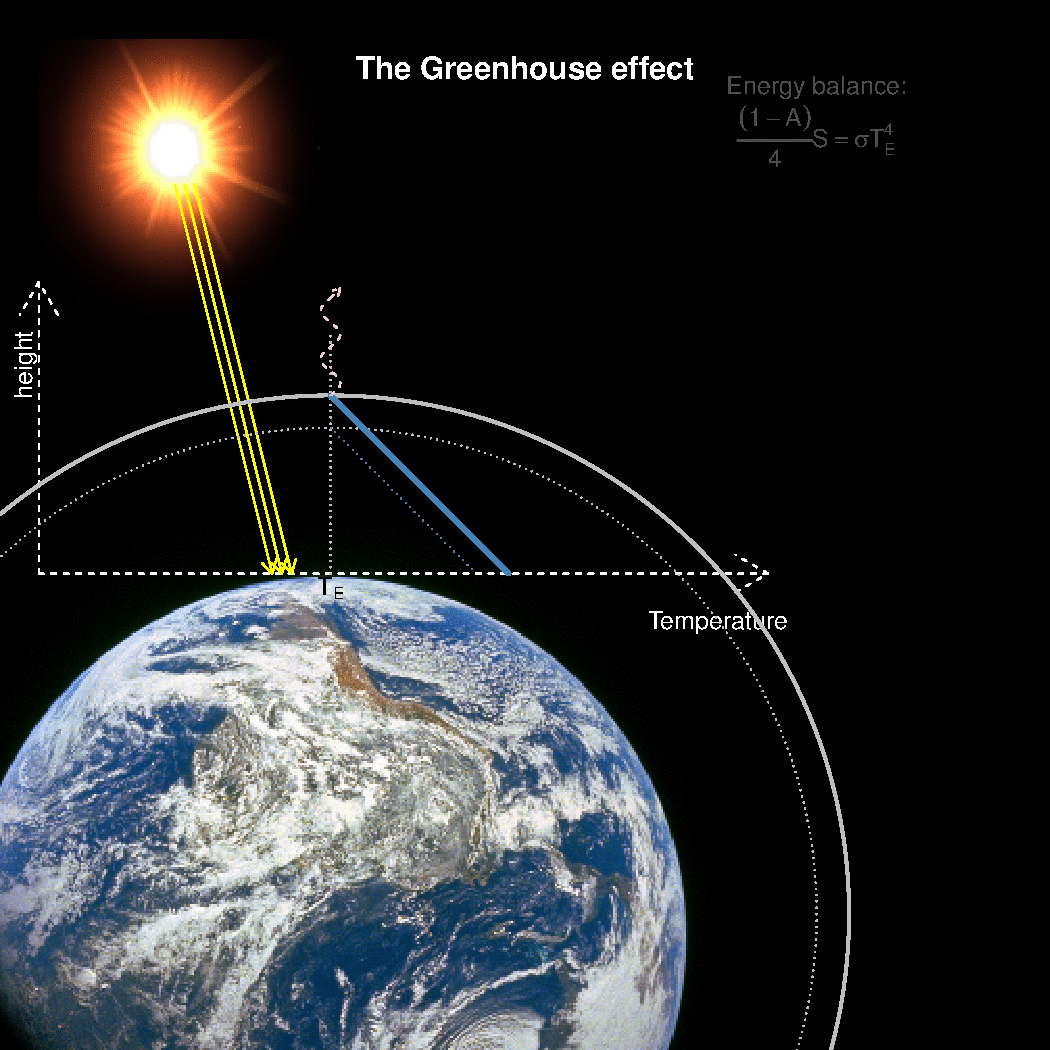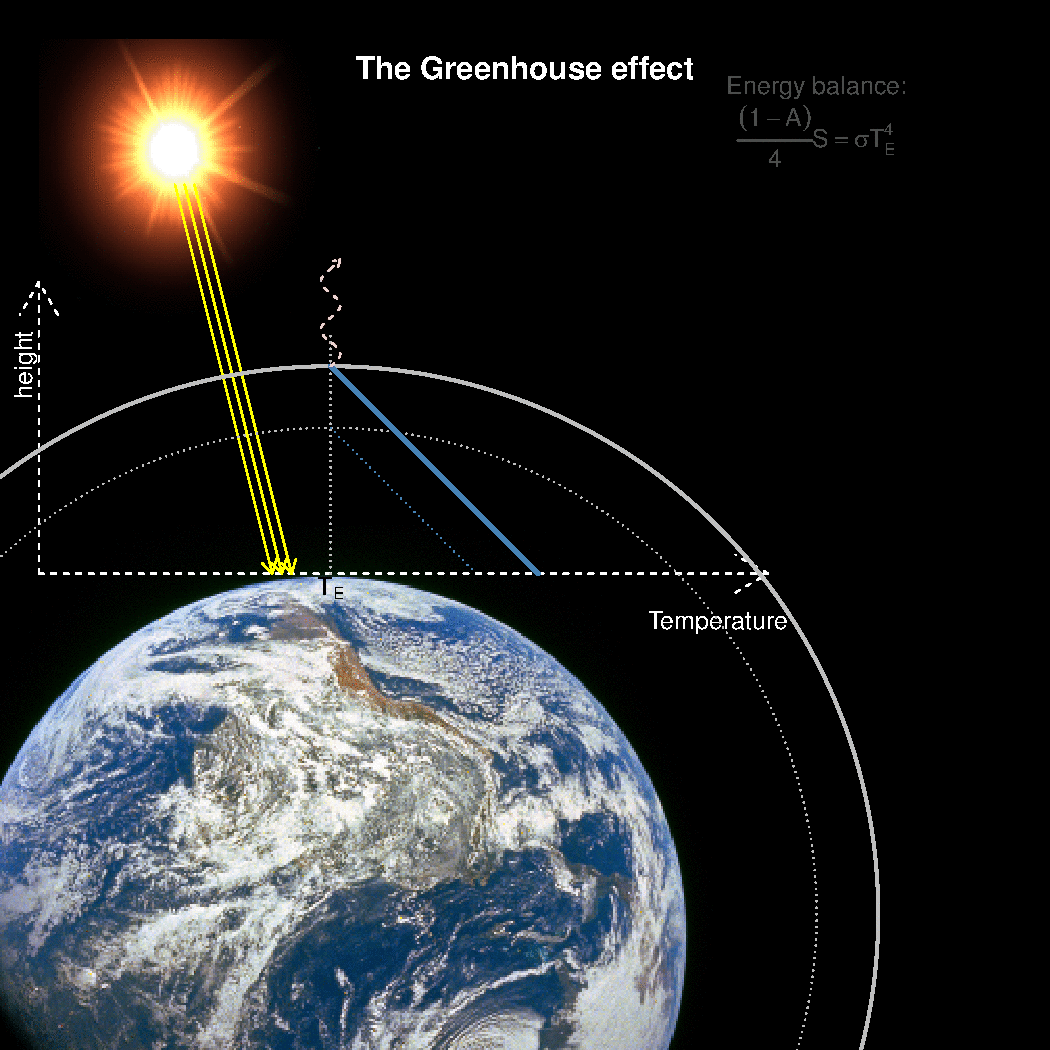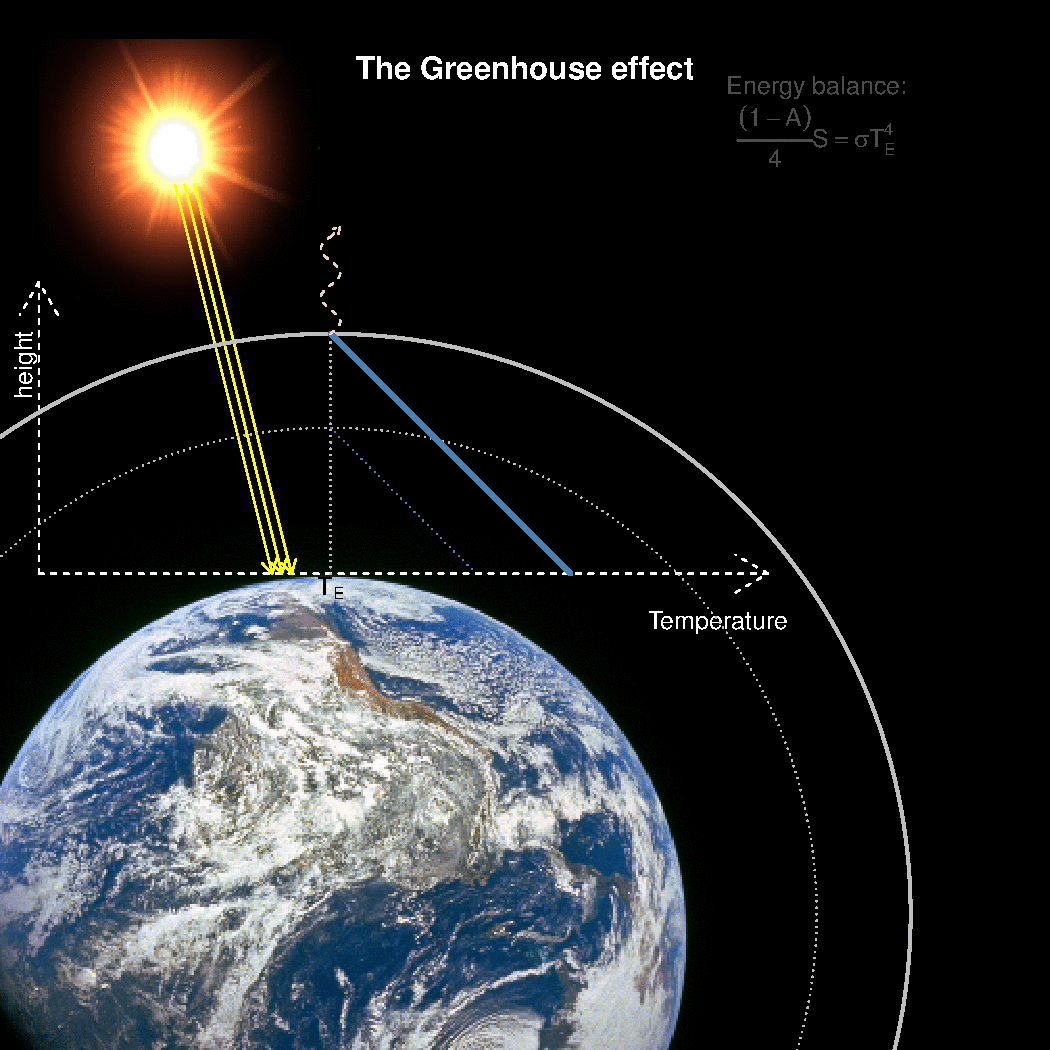



Realclimate What Is The Best Description Of The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
The Greenhouse Effect Life in a greenhouse?The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is originated by gases in the atmosphere which trap energy from the Sun—just like the glass in a greenhouse These gases are called greenhouse gases (GHGs) These gases are water vapor (the most important), ozone, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, all ofAn increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percent
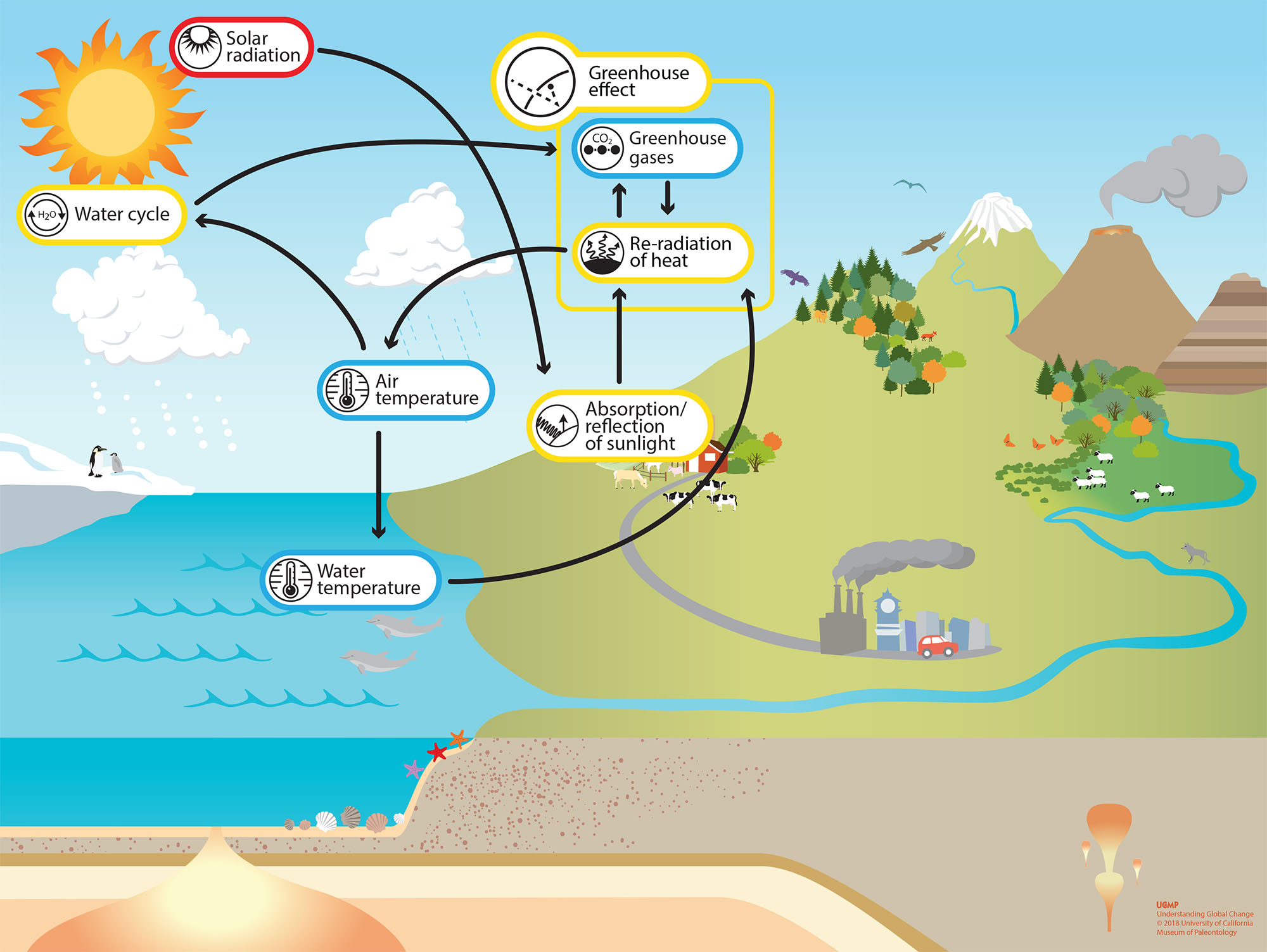



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Understanding Greenhouse Effect Warming Of Earth Through Everyday Examples Youtube
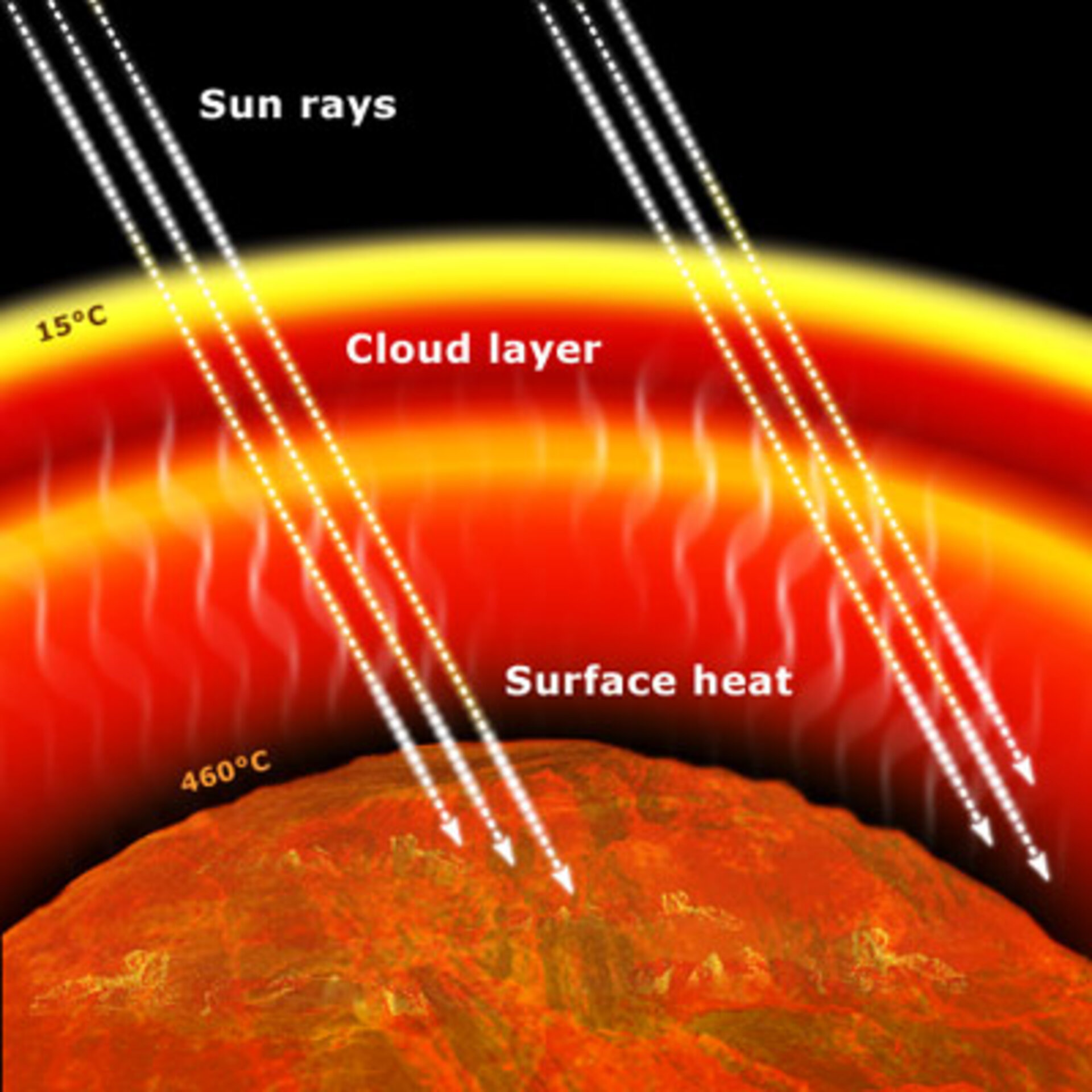
Warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface byGreenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, andIn bright sunshine, the air inside a greenhouse becomes warm The greenhouse glass lets in the sun's light energy and some of its heat energy This heat builds up inside the greenhouse You just showed a small greenhouse effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Blogger




File Greenhouse Effect Png Wikimedia Commons
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapCan help clarify the common confusion and misconception about the greenhouse effect as a natural, not manmade, phenomenon Excellent animation with narrative that discusses what the greenhouse effect is, how humans contribute to it, and how this relates to global climate change The presentation is highly appropriate for kids and includesThe greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know it




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society
This process is known as the natural greenhouse effect and keeps Earth's average global temperature at approximately 15°C (59°F) The Natural Greenhouse Effect Use the buttons below to see an animation of the natural Greenhouse Effect I The sun's visible wavelengths of radiation pass easily through the atmosphere and reach EarthMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides
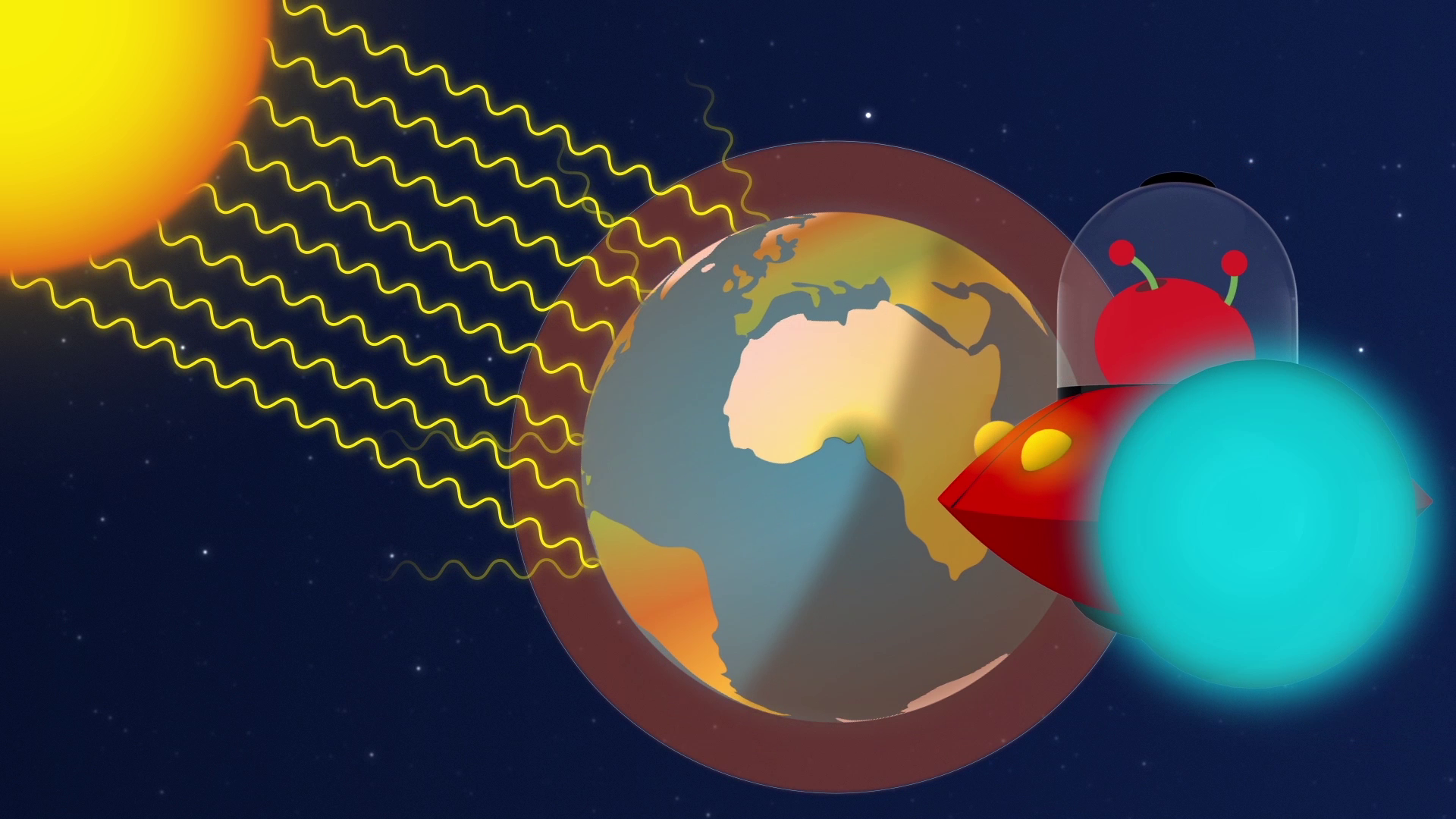



Esa Paxi The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect
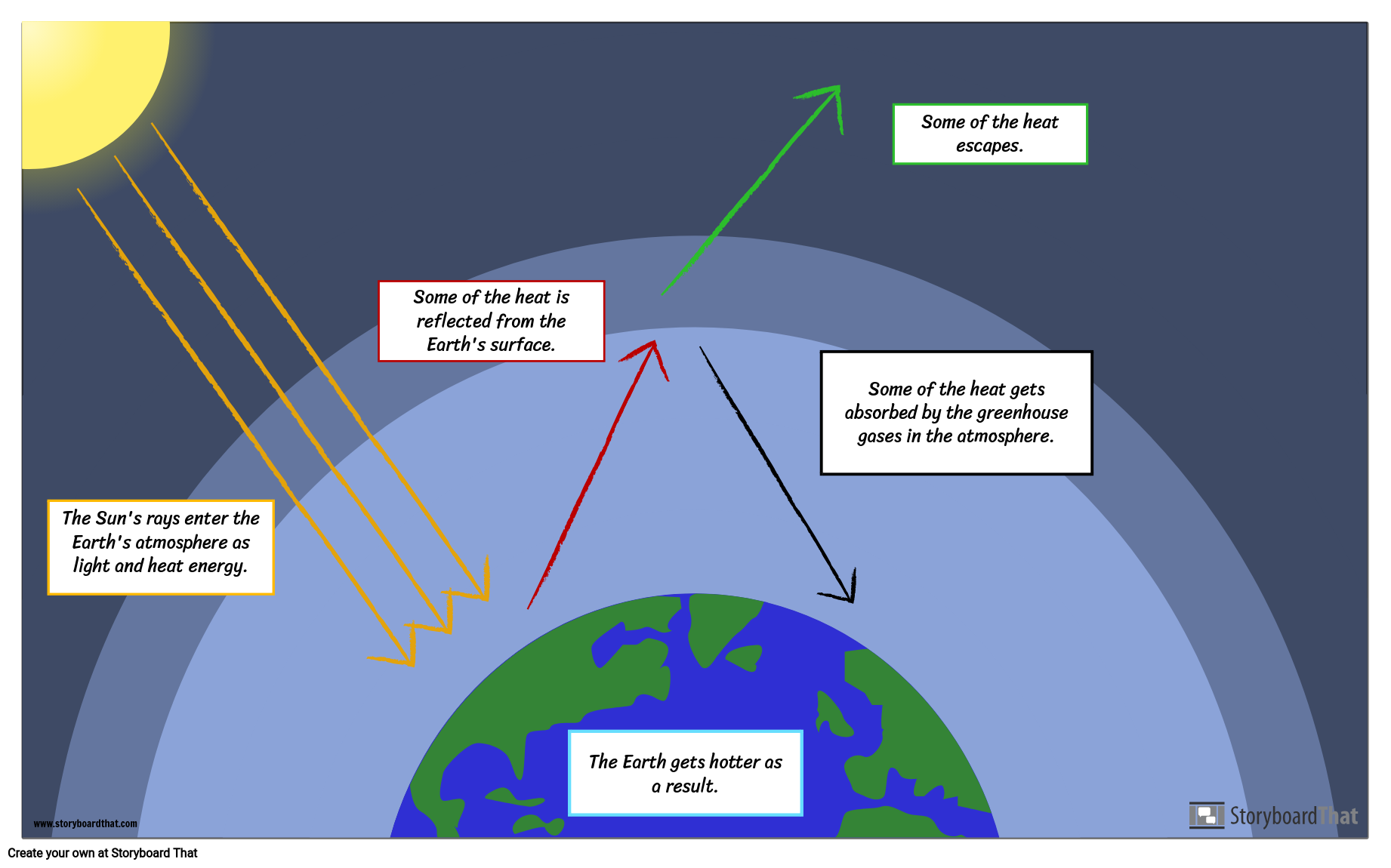
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methaneThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gasesThe greenhouse effect often gets a bad rap because of its association with global warming, but the truth is we couldn't live without it
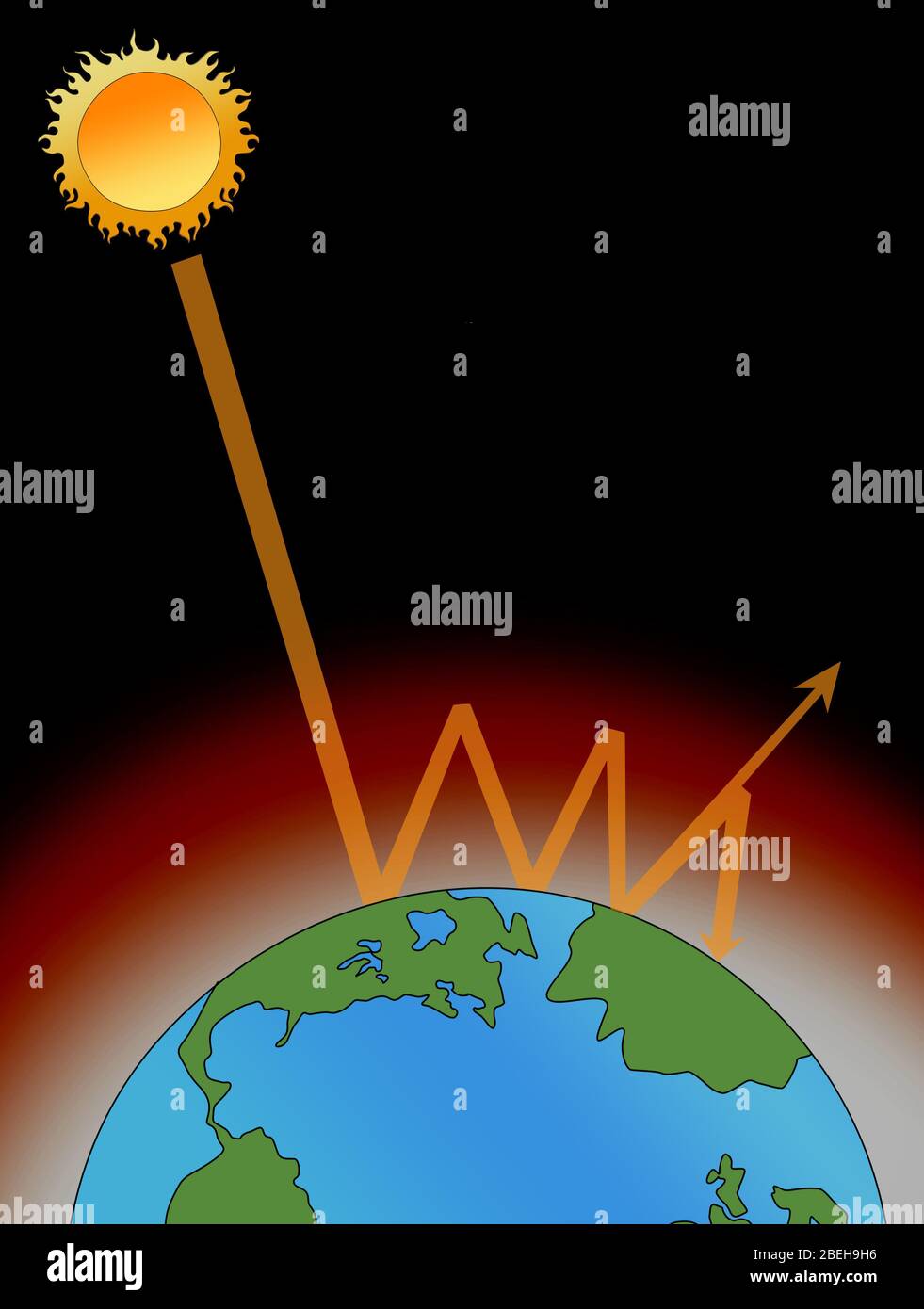



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
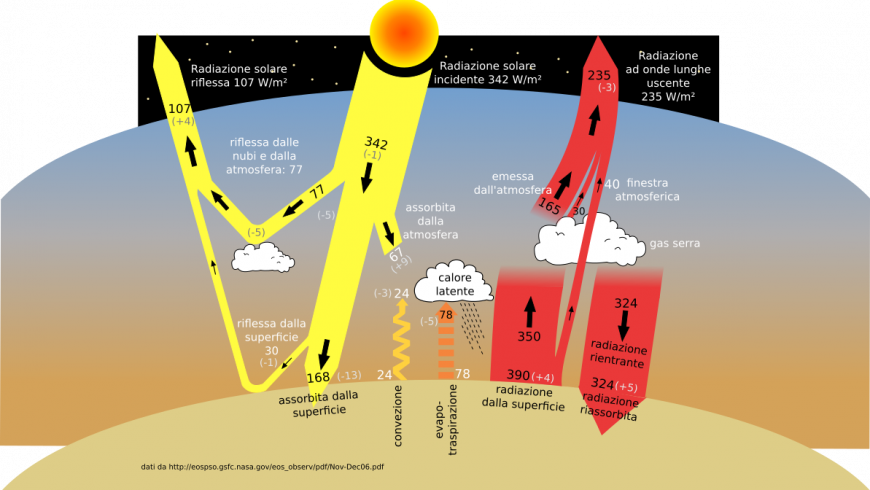



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
Greenhouse gases pose threat to public health — Critics who doubt dire predictions about global warming question how much difference, say, a 2degree temperature increase could mean to the planet According to ron Bernstein, quite a bitGreenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect refers to circumstances where the short wavelengths of visible light from the sun pass through a transparent medium and are absorbed, but the longer wavelengths of the infrared reradiation from the heated objects are unable to pass through that medium The trapping of the long wavelength radiation leads to more heating and a higherThe greenhouse effect definition is the warming of the Earth's atmosphere that is caused by air pollution




What Is The Greenhouse Effect The Environment For Kids Updated Version Youtube




The Greenhouse Effect World101
Greenhouse effect is nothing but the process by which radiation from the planet's atmosphere warms up its surface to a temperature above the atmospheric level The thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directionsThese greenhouse gases absorb heat and radiate some of it back to the earth's surface, causing surface temperatures to be higher than they would otherwise be The most important naturally occurring greenhouse gas is water vapour and it is the largest contributor to the natural greenhouse effectThe Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming How the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environment It absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocks It is the raw material for photosynthesis and its carbon is




Climate And Greenhouse Effect Umweltbundesamt




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence ofSimilarly, but through a different physical process, the Earth's greenhouse effect warms the surface of the planet Without the natural greenhouse effect, the average temperature at Earth's surface would be below the freezing point of water Thus, Earth's natural greenhouse effectmakes life as we know it possible However, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
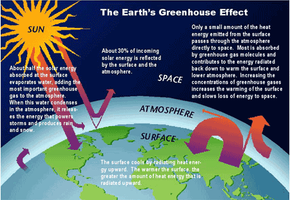



The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
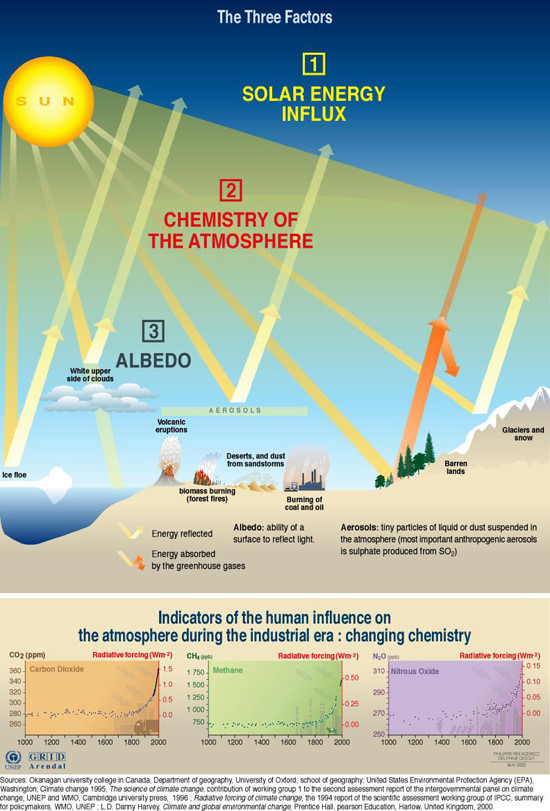



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




6 3 The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Climate Change Organization
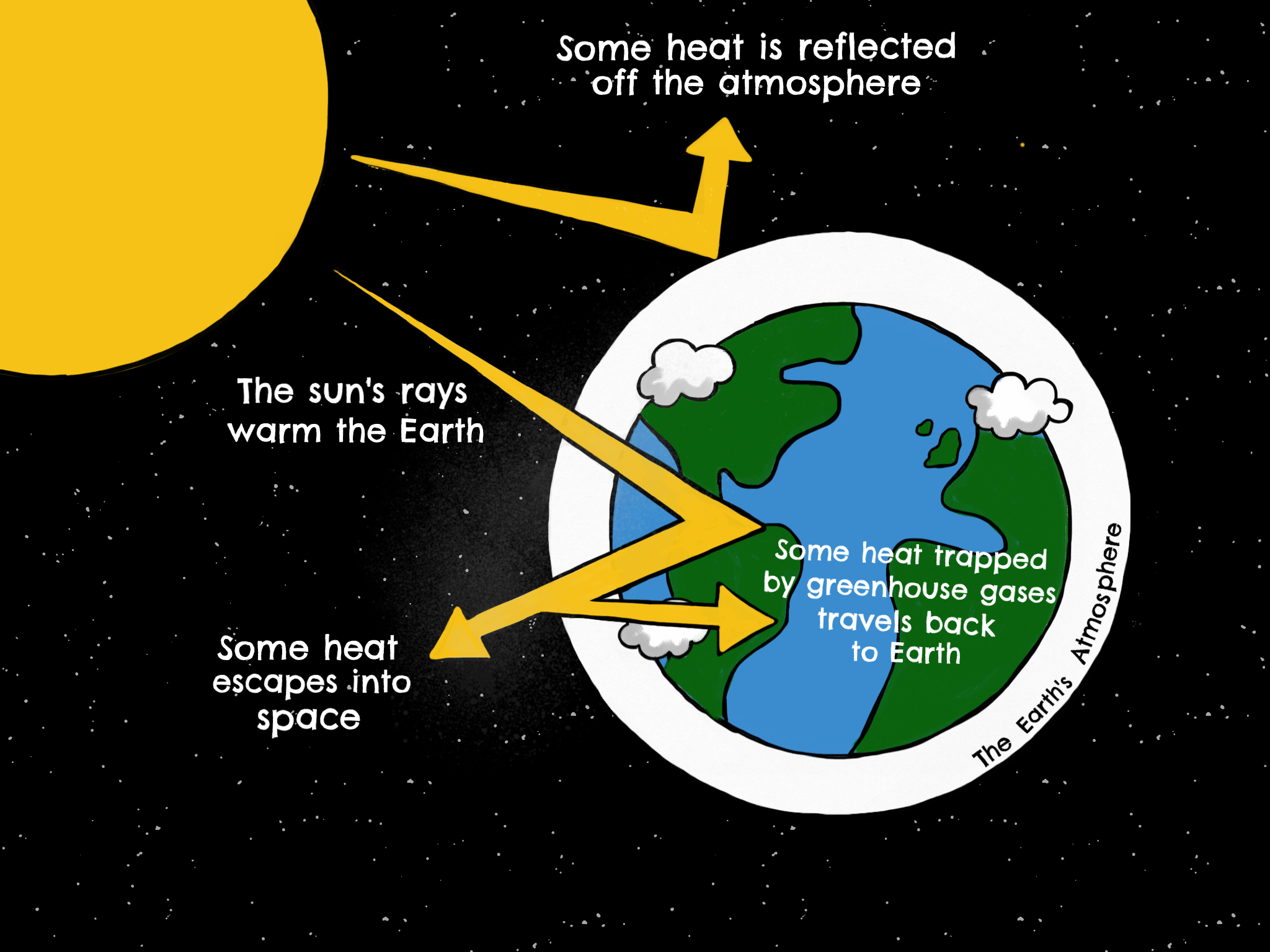



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change
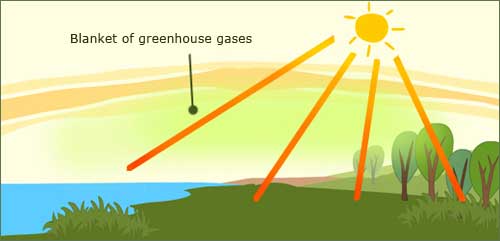



How Does The Greenhouse Effect Happen Eschooltoday




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Geolog 1 Years Of The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Its Mechanism And Importance Technology Times



3




Greenhouse Effect Top 3 Advantages And Disadvantages



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Esa Greenhouse Effects Also On Other Planets




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Causes And Examples Market Business News



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Effect
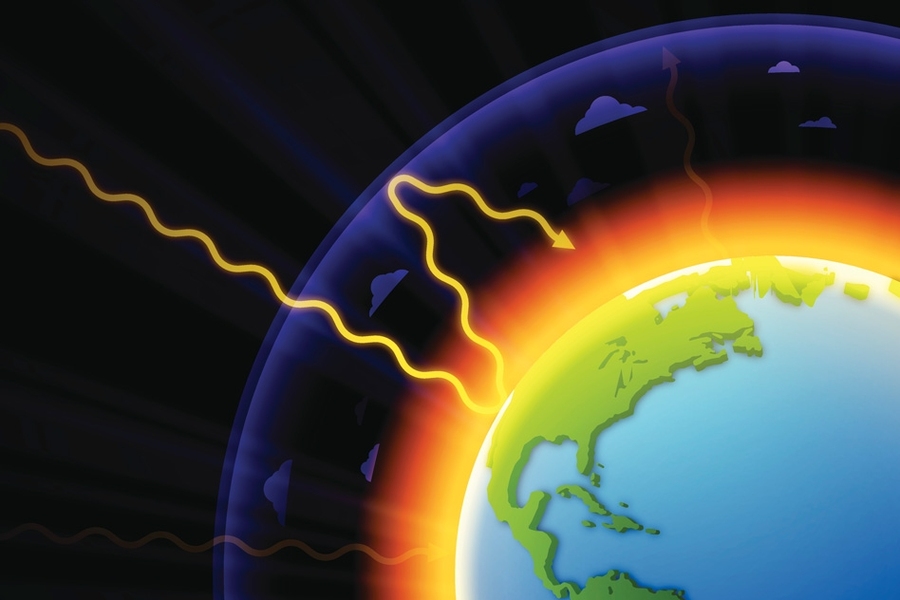




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts




The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Warming Global New Light Of Myanmar




Greenhouse Effect Illustration Stock Image C050 7564 Science Photo Library




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Greenhouse Effect
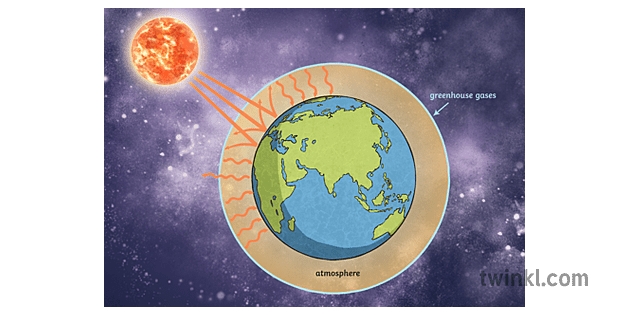



Greenhouse Effect رسم Twinkl
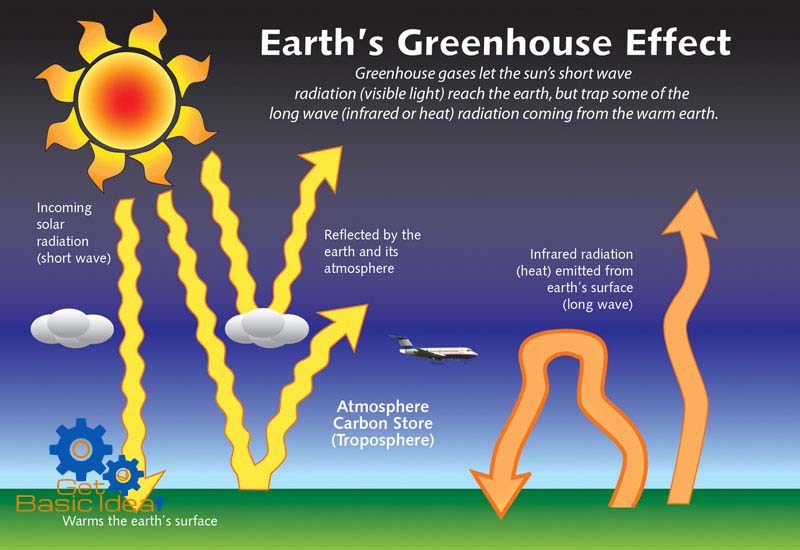



Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Chemistry




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
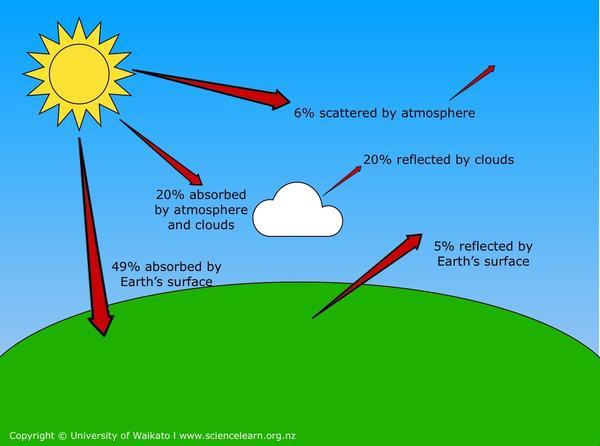



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




What Causes The Greenhouse Effect Greentumble



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Infographic Royalty Free Vector Image




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov
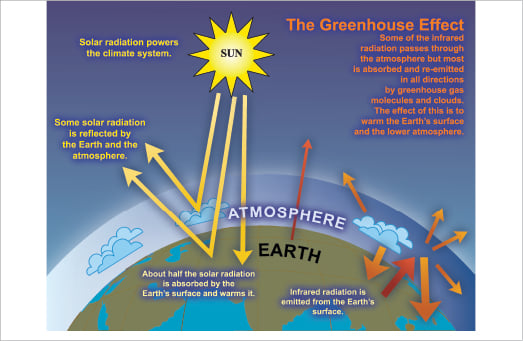



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




6 2 The Greenhouse Effect Global Climate Change Organization




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission



Greenhouse Effect Body Used Water Process Earth Plants Form Energy Gas




Explaining The Greenhouse Effect Sustainability Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



Q Tbn And9gctaj8wii876qu Vg Qiwf0vbxzn5m2dj2uyfahncczk01qi3 Z7 Usqp Cau




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
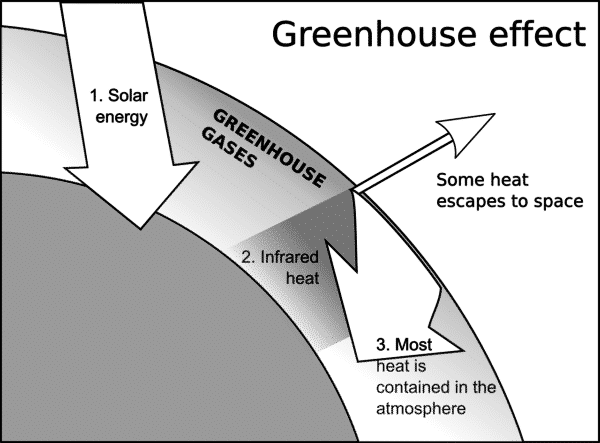



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




Greenhouse Effect How Does Climate Change Work
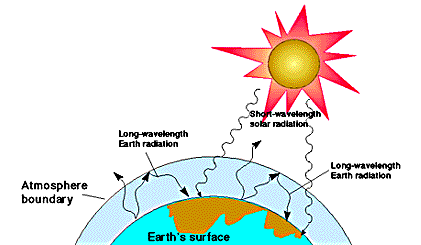



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases
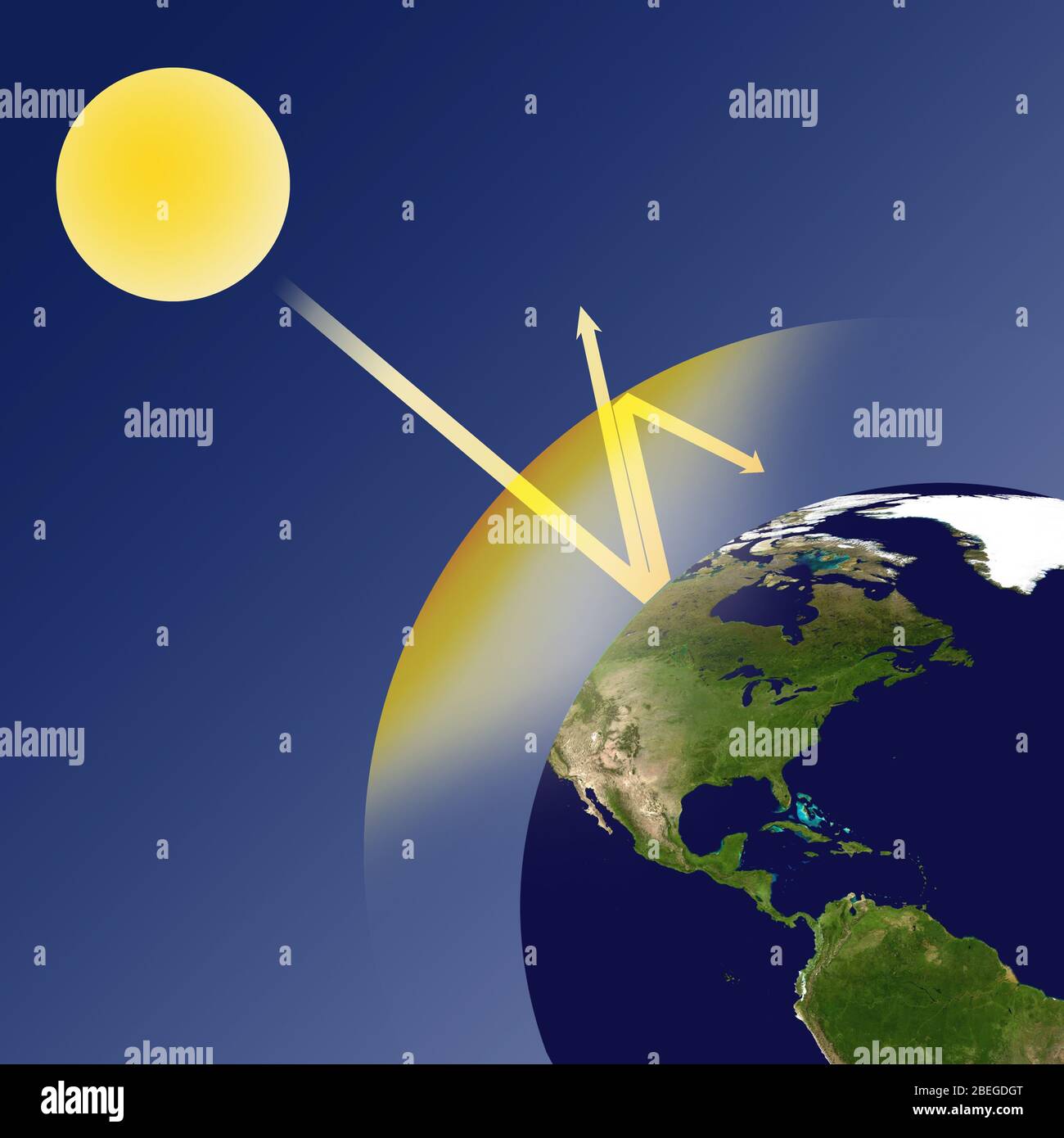



Greenhouse Effect Stock Photo Alamy
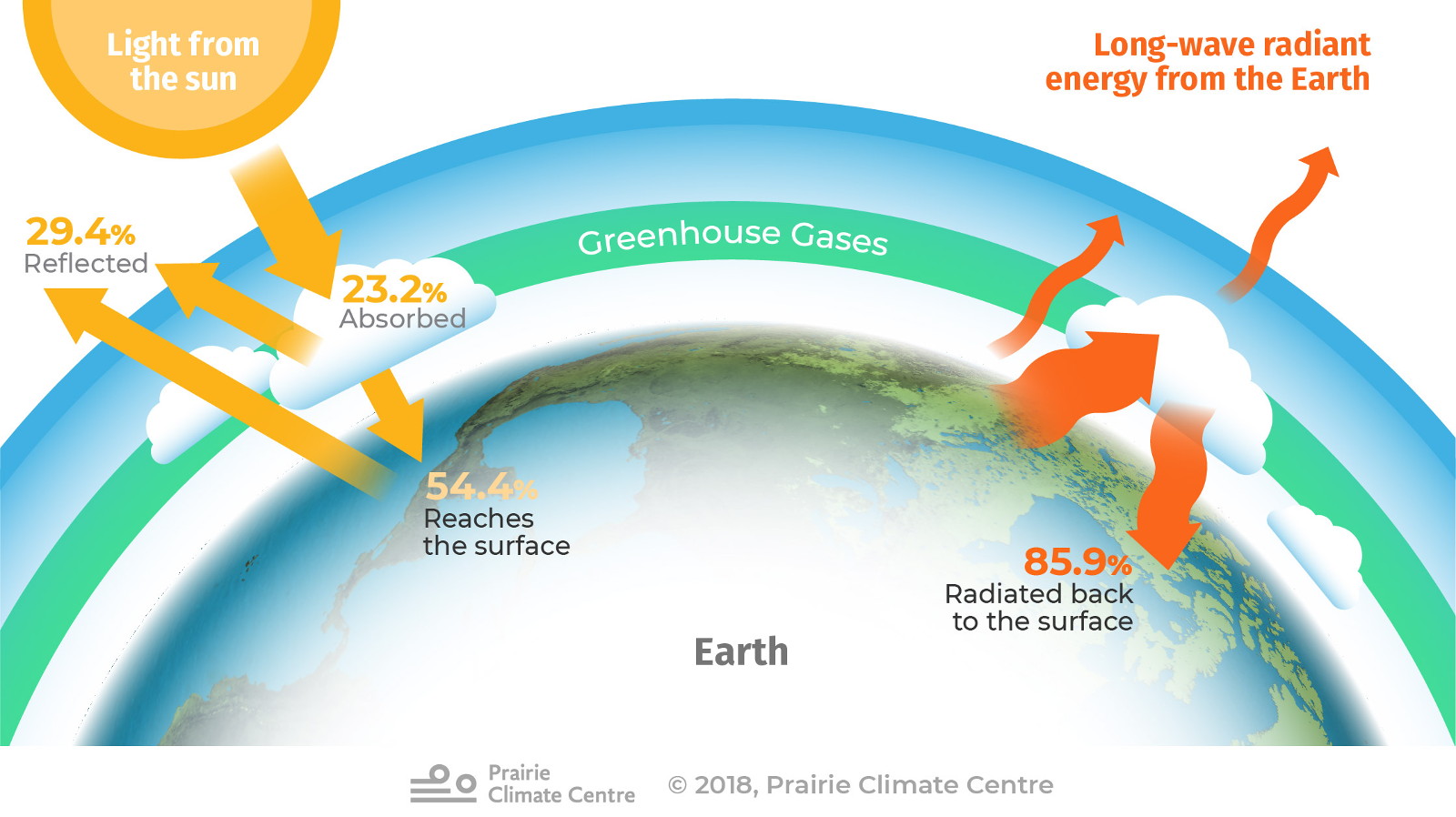



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
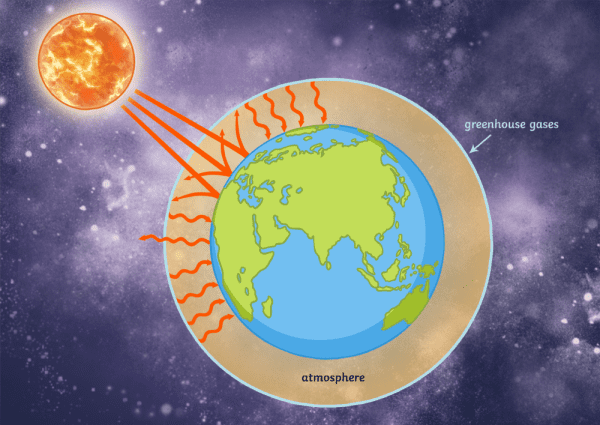



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Effect Earth Warm And Other Effects Tech Spectro




Scheme Of Greenhouse Effect Vector Image By C Ziablik Vector Stock
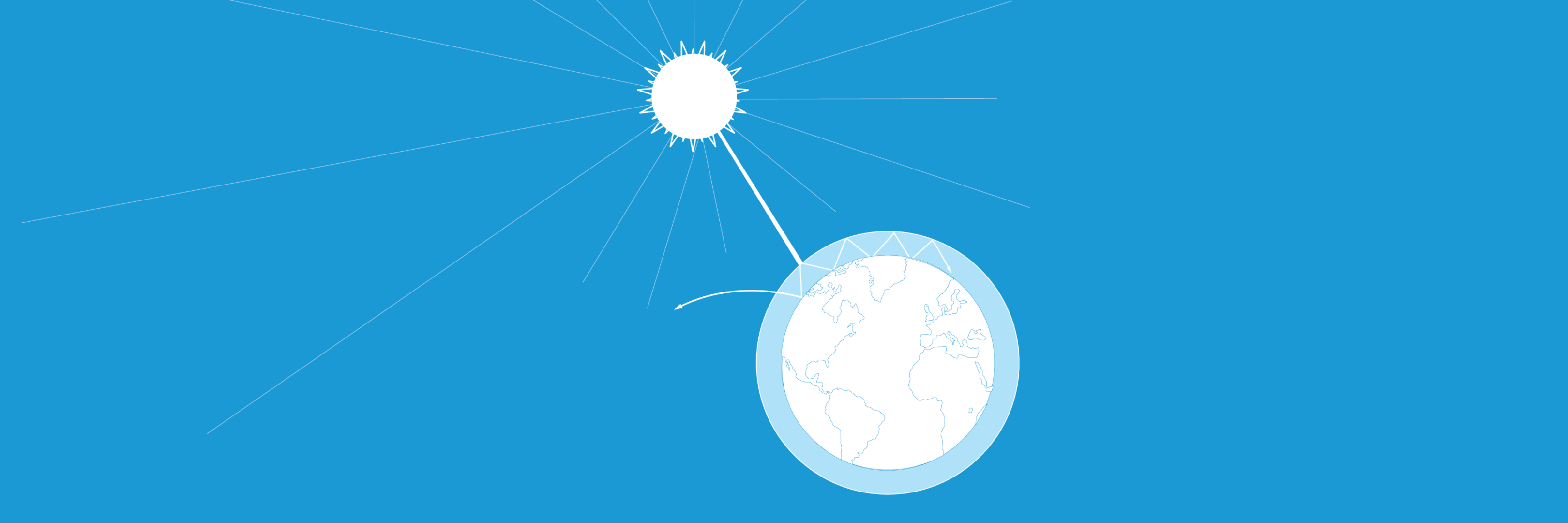



Esa The Greenhouse Effect And Its Consequences Investigating Global Warming Teach With Space G03



19 Internal Shell Report The Greenhouse Effect
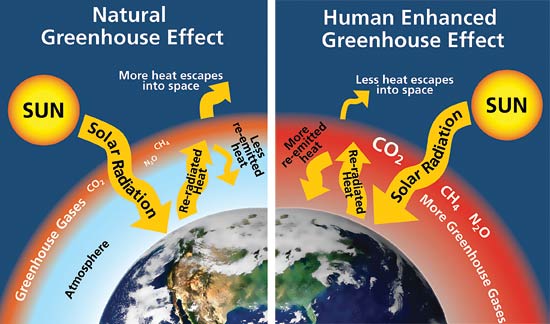



Greenhouse Effect Climate Theory
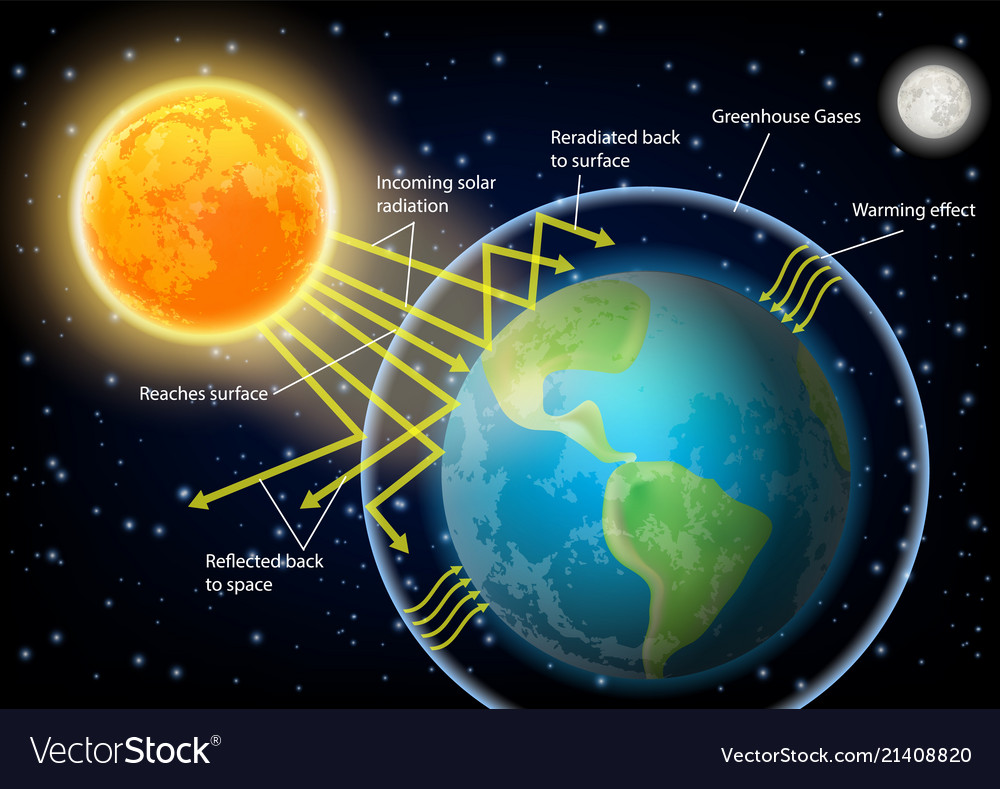



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Of Earth Stockvectorkunst En Meer Beelden Van Fotografische Effecten Istock




What Causes The Greenhouse Effect And What Are The Consequences Eden Springs
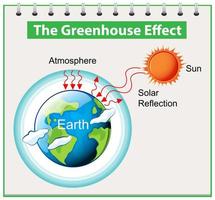



Greenhouse Effect Vector Art Icons And Graphics For Free Download




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Extended Definition The Greenhouse Effect Cleanairdawson
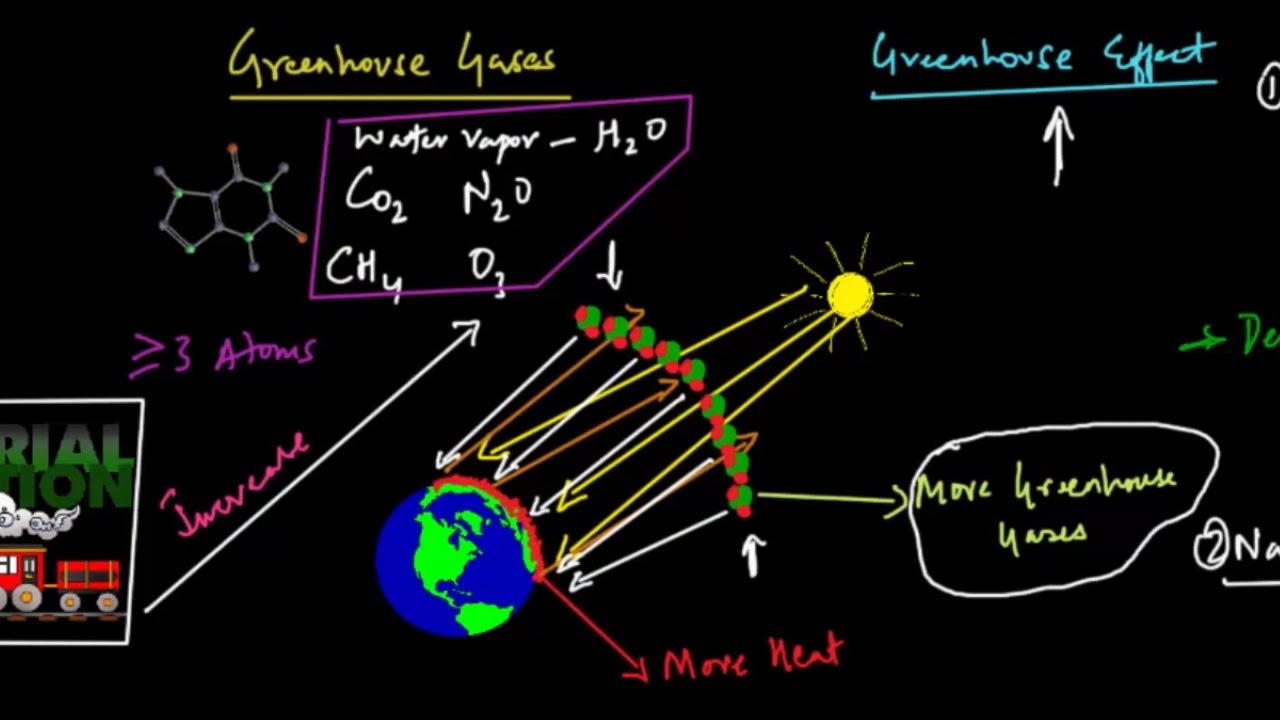



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Blog Nigurha Com Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Greenhouse Gases




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram



1
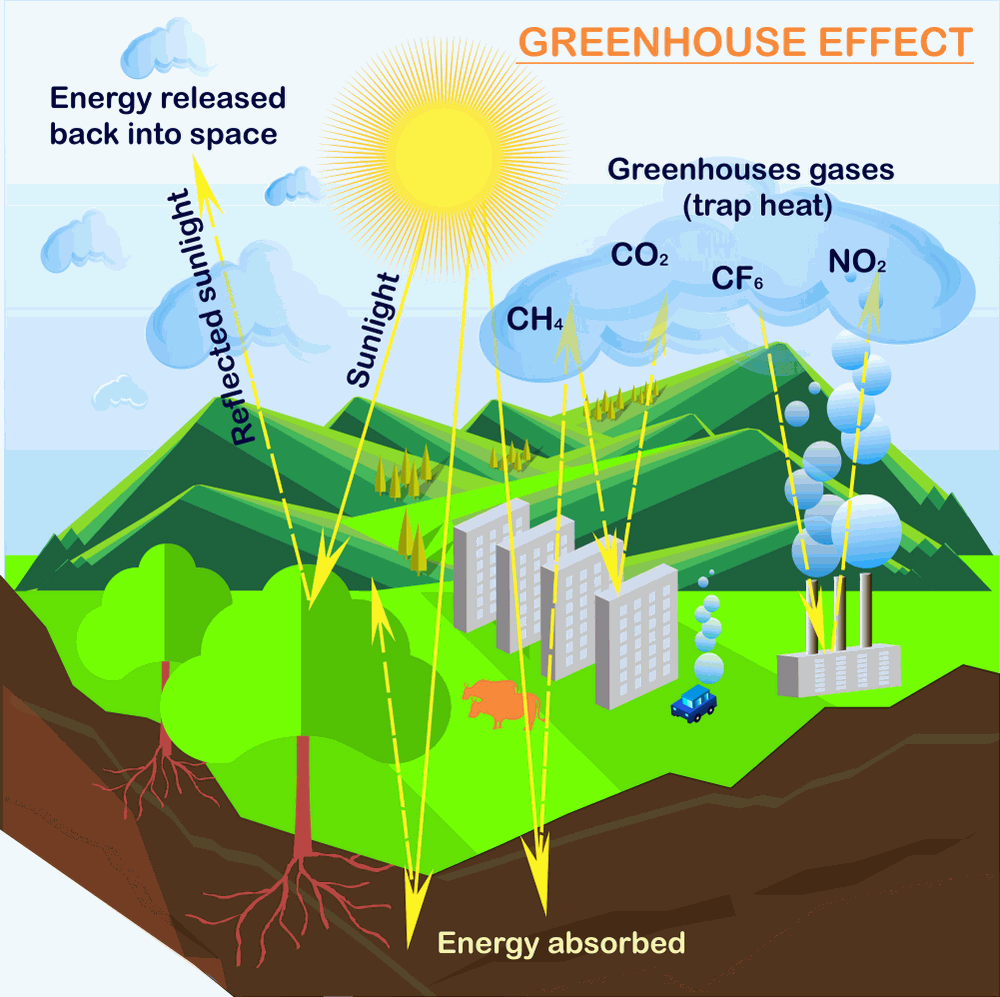



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




The Greenhouse Effect Epthinktank European Parliament



Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
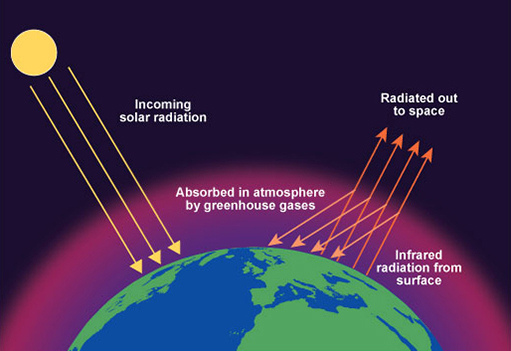



Week 7 The Special Ones 2 2 The Greenhouse Effect Openlearn Open University Exo 1
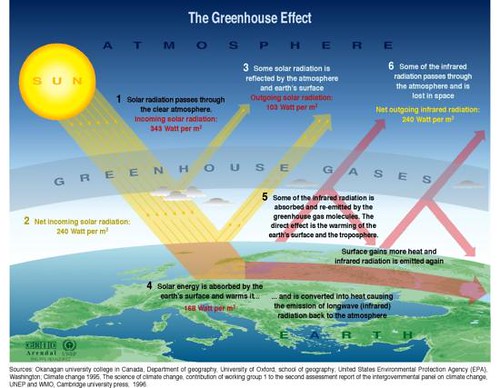



Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿